The cleaning and disinfection process in a traditional system consists of a complex series of operations and steps that typically involve long times, large volumes of water, and large amounts of energy.
Hydrodynamic cavitation has found its way into a wide range of applications, including the reduction of heat-induced contamination of milk.
The motion induced by cavitation ultrasound prevents molecules from remaining on the surface long enough to deposit as a film around the heating surface.
Pre-treatment of whey protein concentrate (WPC) with cavitation ultrasound prior to ultrafiltration increases membrane life by reducing pore clogging, thereby retarding fouling growth.
A higher solids content in the fluid further improves the reduction of pore clogging and fouling growth.
The concentration of permeated proteins remained unchanged under all test conditions.
Numerous studies and specific pilot plants have demonstrated the potential application of ultrasound in the WPC process also especially for reducing energy consumption in ultrafiltration, since cavitation reduces the viscosity of the feed solution.
The cavitation effect leads to a decrease in the number of cleaning cycles required for complete membrane cleaning.
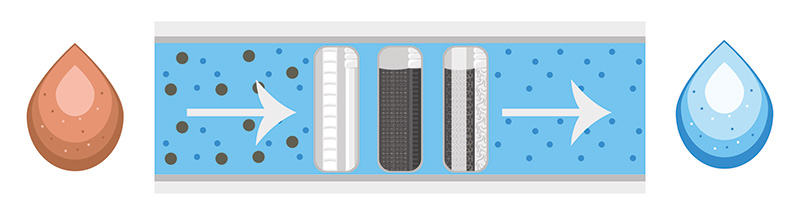
This application has also proven to be effective in the pretreatment of desalination solutions in reverse osmosis processes.
Due to its strength, hydrodynamic cavitation can be used for the cleaning of membranes soiled with whey and has shown better flow recovery after fouling compared to traditional cleaning systems.
Furthermore, a synergistic effect of the combination of hydrodynamic cavitation and surfactants has been observed.
The cavitation cleaning system did not cause any damage to the membrane surface even after repeated cleaning over months. Furthermore, the application of cavitation at room temperature in combination with various cleaning agents reduces cleaning times.