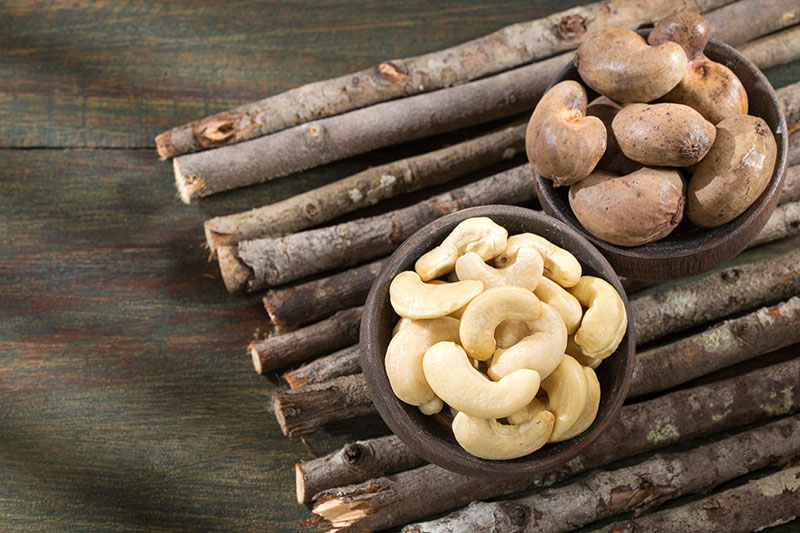
CNSL (Cashew nutshell liquid) is a natural resin with a yellowish sheen found in the honeycomb structure of the cashew nut shell and is a byproduct of cashew nut processing.
The percentage of CNSL is approximately 15 – 30% of the weight of the cashews. Approximately 3.3 kg of cashew shells are needed to produce 1 kg of CNSL, and approximately 20% of the nut shell oil is found in raw cashews.
To extract it, we start by pre-treating the biomass of cashew shells.
There are numerous pretreatment techniques, each with advantages and disadvantages. They can be substantially divided into four categories: mechanical, thermal, chemical and pyrolytic extraction.
CNSL can be mechanically extracted using a screw press or panel. Using this technique, natural CNSL is extracted from raw cashew shells by applying intense pressure. The extraction process is quick and simple and produces high-quality CNSL.
By roasting nuts at 180–185°C, thermal extraction causes the anacardic acids to decarboxylate, thus breaking the shell cells and releasing the oil. Open pan roasting, drum roasting, and hot oil roasting are all thermal extraction methods. The extraction process uses higher temperatures to convert anacardic acid into cardanol. Accordingly, a thermal extraction strategy is applied when the target is cardanol-rich CNSL. Distillation of this material provides a technical distillate CNSL containing 78% cardanol and 8% cardanol (cardanol has one more hydroxyl group than cardanol). This process also reduces the degree of thermal polymerization of the unsaturated alkyl phenols present in CNSL.
Organic solvents are used in chemical pretreatment processes to alter the structural integrity of biomass by disrupting intra- and interpolymer bonds between organic components. Cold-solvent-extracted CNSL is mainly composed of anacardic acids (70%), [51] cardol (18%), and cardanol (5%).