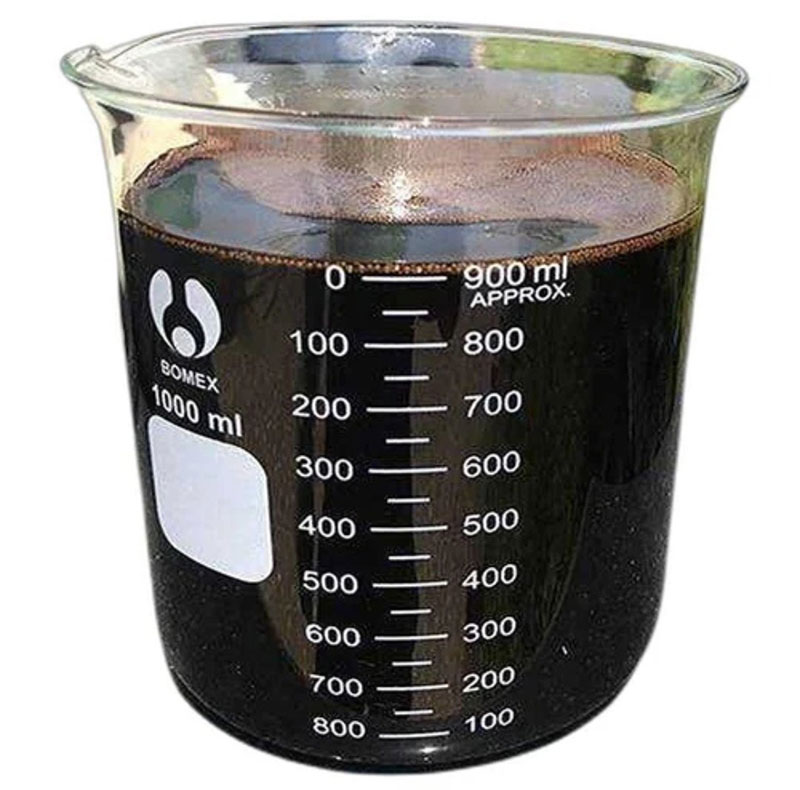
CNSL can be used as a resin for carbon composite products. CNSL-based novolac is another versatile industrial monomer derived from cardanol typically used as a cross-linking agent for epoxy matrices in composite applications providing good thermal and mechanical properties to the final composite material.
This natural oil phenol has interesting chemical structural characteristics that can be modified to create a broad spectrum of biologically derived monomers. These take advantage of the chemically versatile construct, which contains three functional groups: the aromatic ring, the hydroxyl group and the double bonds in the flanking alkyl chain.
These include polyols, which have recently seen increased demand due to their biological origin and key chemical attributes such as high reactivity, range of functionality, reduction of blowing agents and natural flame retardant properties in the field of rigid polyurethanes, aided by their inherent phenolic nature and a greater number of reactive units per unit mass.