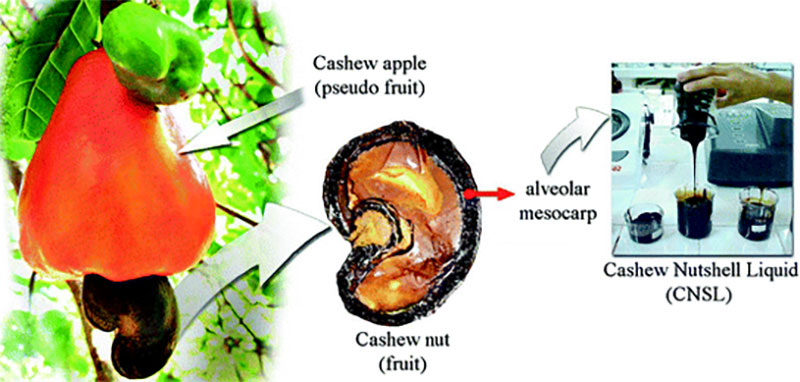
If the target is anacardic acid-rich CNSL, solvent extraction is the preferred technique because it usually produces more CNSL than other techniques.
Since organic solvents are dangerous, their use in the extraction process leads to a number of unwanted effects on both the environment and human health. Cost is another issue due to the large quantities of solvents needed in many cases.
To overcome these problems, the extraction takes place via hydrodynamic cavitation in water inside the EMPOWERING DEVICE: thus both the mechanical and thermal effects are combined. In fact, the bubbles that form during the physical phenomenon explode and generate very high but limited temperatures and also generate micro-hydro jets that destroy the cell walls. The system has been used for the extraction of olive oil with notable advantages; in fact, the maximum temperature that the solution can reach is 30°C, a temperature that avoids the deterioration of thermosensitive molecules such as polyphenols.
The properties of CNSL acquired through the various extraction procedures vary to a certain extent: they are in effect extracts with different properties and quantities.
The cold pressing solvent extraction method of CNSL needs to be elaborated to remove metallic impurities and residual sulfur compounds.
The properties of this treated CNSL differ from those of raw CNSL. With a better understanding of each extraction process, an appropriate strategy can be chosen to obtain a high yield of CNSL, a desired ingredient in CNSL, or favorable properties of CNSL.
Before commercial use, CNSL is often refined by chemical treatment with sulfated hydrocarbons and sulfuric acid to remove sulfides, nitrogenous chemicals, and minerals, which also affect the quality of the nutshell liquid.