TPE is a rubber-like material, which can be processed with thermoplastic technologies such as injection molding, co-molding or extrusion. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are compounds made of hard thermoplastic materials such as PP, PBT and PA, in combination with a soft and rubbery material and often also with additives such as oils and fillers.
More simply, it is a polymeric mixture or compound that, above its melting temperature, has a thermoplastic character that allows it to be shaped while, within its temperature range, it has elastomeric behavior without cross-linking.
This process is reversible and the products can be reworked and reshaped making them particularly attractive as "modern" materials to replace "dated" single-use materials.
Among the main advantages of thermoplastic elastomers is the greater ease in processing them (and the lower energy expense compared to thermosets), with conventional thermoplastic processes such as injection molding, extrusion, thermoforming and blow molding. Furthermore, TPEs can be easily colored and overmolded to various thermoplastics, with good adhesion.
TPEs are a unique class of engineering materials that combine the look, feel and elasticity of conventional thermoset rubber with the processing efficiency of plastic.
TPEs are used where conventional elastomers are unable to provide the range of physical properties needed by the product. These materials find widespread application in the automotive sector and in the household appliance sector.
TPE is commonly used to make suspension bushings for automotive applications due to its greater resistance to deformation than regular rubber bushings.
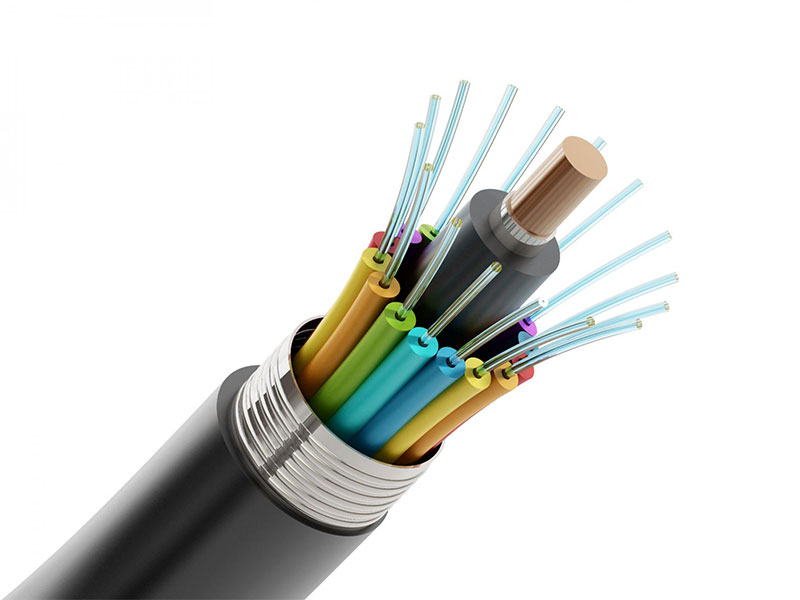
Thermoplastic materials have seen growth in the heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) industry due to their functionality, cost-effectiveness and adaptability in modifying plastic resins into a variety of covers, fans and housings. TPE can also be used in medical devices, sheaths and internal insulation of electrical cables, sex toys and some headphone cables
Another area of application for TPE material is now 3D printing, for which materials with rubber-like properties were out of the question for a long time. Flexible TPE filaments are used here to produce flexible or customizable parts, such as smartphone covers. Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is the most commonly used material for 3D printing. On the other hand, for specialized applications such as the processing of PLA, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polycarbonate (PC), the TPS from Kuraray are particularly well-suited.